Pimpl 编程技巧
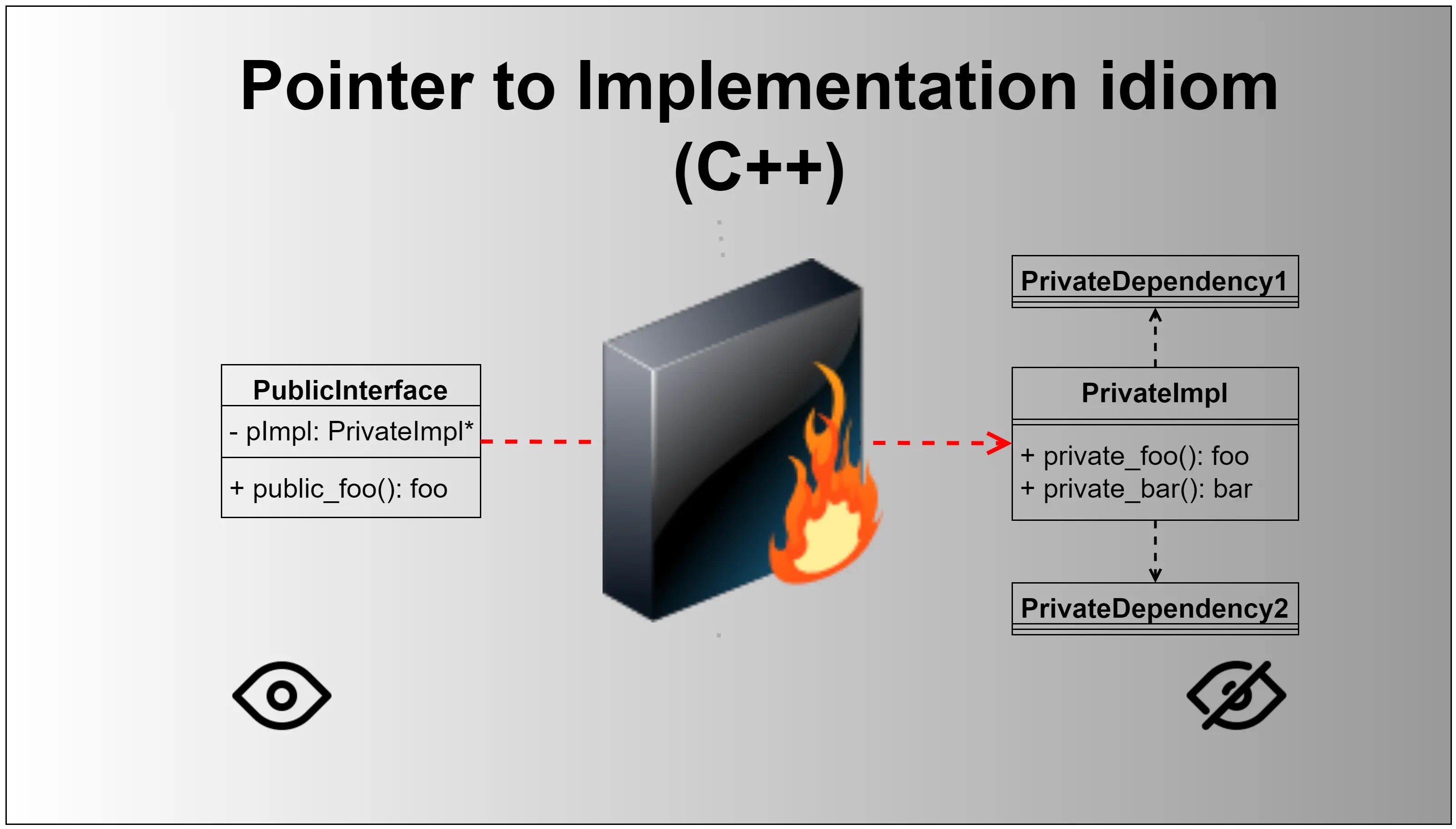
Pimpl(Pointer to Implementation)是一种C++编程技术,用于实现数据封装和减少编译依赖。它的基本思想是将类的实现细节放在一个单独的类中,并通过指针在主类中引用这个实现类。这种方式有几个优点:
- 减少编译时间:当实现细节发生变化时,只需重新编译实现类,而不需要重新编译使用该类的所有代码。
- 隐藏实现细节:用户只需了解接口,而不需要关心具体的实现,这有助于提升代码的封装性和可维护性。
- 降低类的大小:主类的大小会变得更小,因为它只包含指向实现的指针,而不是所有的成员变量。
Pimpl模式通常在库开发中使用,以便提供稳定的API,同时允许内部实现的灵活性。
示例
下面是demo.h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
#ifndef __DEMO_H__
#define __DEMO_H__
#include <memory>
class Demo
{
public:
Demo(int a, int b);
~Demo();
int add();
private:
class Impl;
std::unique_ptr<Impl> pimpl;
};
#endif // __DEMO_H__
下面是demo.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
#include "demo.h"
class Demo::Impl
{
private:
int x;
int y;
public:
Impl(int a, int b)
: x(a)
, y(b)
{}
int add()
{
return x + y;
}
};
Demo::Demo(int a, int b)
: pimpl(std::make_unique<Impl>(a, b))
{}
Demo::~Demo()
{
}
int Demo::add()
{
return pimpl->add();
}
说明
将类的实现细节隐藏在一个单独的Impl类中,并通过指针在主类中引用这个实现类。这样,我们就实现了Pimpl模式!
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权